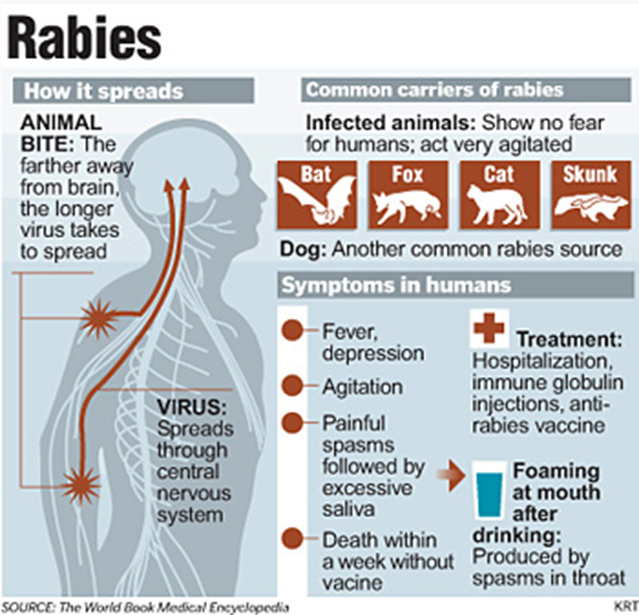
Rabies is an infectious viral disease that is almost always fatal following the onset of clinical signs. In more than 99% of human cases, the rabies virus is transmitted by domestic dogs. Rabies affects domestic and wild animals, and is spread to people through bites or scratches, usually via saliva.
Prevention of Rabies
1. Eliminating rabies in dogs
Rabies is a vaccine-preventable disease. Vaccinating dogs is the most cost-effective strategy for preventing rabies infection in humans
2. Preventive immunization in people :
Who should be vaccinated?
•laboratory workers who may be required to handle samples of the rabies virus
•people handling bats
•people working in close contact with animals, such as vets or animal handlers at zoos
It is also recommended for:
•people travelling to an area for one month or more where rabies is common in animals and there is no access to prompt and safe medical care
•people travelling to an area where rabies is common and taking part in activities that expose them to rabies, such as trekking in a jungle
Symptoms
1) Incubation period :1 year
2) Initial symptoms :
- Fever
- Pain
- Unusual or unexplained tingling, pricking or burning sensation (paraesthesia) at the wound site.
- CNS : signs of hyperactivity, excited behaviour, hydrophobia and sometimes aerophobia.
- Cardiorespiratory arrest.
Paralytic rabies accounts for about 30% of the total number of human cases. This form of rabies runs a less dramatic and usually longer course than the furious form. The muscles gradually become paralyzed, starting at the site of the bite or scratch. A coma slowly develops, and eventually death occurs. The paralytic form of rabies is often misdiagnosed, contributing to the under-reporting of the disease.
Diagnosis
Human rabies can be confirmed intra-vitam and post mortem by various diagnostic techniques aimed at detecting whole virus, viral antigens or nucleic acids in infected tissues (brain, skin, urine or saliva).
Transmission
Following a deep bite or scratch by an infected animal. Dogs are main host and transmitter of rabies.
Transmission can also occur when infectious material – usually saliva – comes into direct contact with human mucosa or fresh skin wounds. Human-to-human transmission by bite is theoretically possible but has never been confirmed.
Rarely, rabies may be contracted by inhalation of virus-containing aerosol or via transplantation of an infected organ. Ingestion of raw meat or other tissues from animals infected with rabies is not a source of human infection.
Treatment of Rabies
There's no specific treatment for rabies infection. Though a small number of people have survived rabies, the disease is usually fatal.
Local treatment of the wound
This involves first-aid of the wound that includes immediate and thorough flushing and washing of the wound for a minimum of 15 minutes with soap and water, detergent, povidone iodine or other substances that kill the rabies virus.









.jpeg)














